|
An Illinois Private Fights At The Hornet's Nest
by Leander Stillwell
The Story of a Common Soldier of Army Life in the Civil War, 1861-1865
Published in 1920
| Battle of Shiloh Hornet's Nest Map |
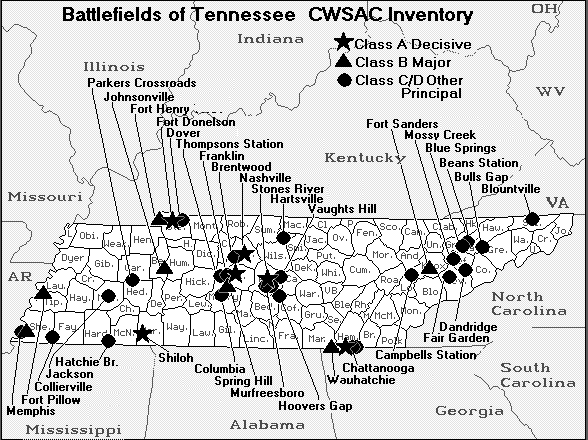
|
| Civil War Shiloh Hornets Nest Battlefield Map |
[April 6, 1862]
We had "turned out" about sunup, answered to roll-call,
and had cooked and eaten our breakfast. We had then gone to work, preparing for the regular Sunday morning inspection, which
would take place at nine o'clock. The boys were scattered around the company streets and in front of the company parade grounds,
engaged in polishing and brightening their muskets, and brushing up and cleaning their shoes, jackets, trousers, and clothing
generally.
It was a most beautiful morning. The sun was shining brightly through the
trees, and there was not a cloud in the sky. It really seemed like Sunday in the country at home. During week days there was
a continual stream of army wagons going to and from the landing, and the clucking of their wheels, the yells and oaths of
the drivers, the cracking of whips, mingled with the braying of mules, the neighing of the horses, the commands of the officers
engaged in drilling the men, the incessant hum and buzz of the camps, the blare of bugles, and the roll of drums,--all these
made up a prodigious volume of sound that lasted from the coming-up to the going-down of the sun. But this morning was strangely
still. The wagons were silent, the mules were peacefully munching their hay, and the army teamsters were giving us a rest.
I listened with delight to the plaintive, mournful tones of a turtle-dove in the woods close by, while on a dead limb of a
tall tree right in the camp a wood-pecker was sounding his "long roll" just as I had heard it beaten by his Northern brothers
a thousand times on the trees in the Otter Creek bottom at home.
Suddenly, away off on the right, in the direction of Shiloh church, came a
dull, heavy "Pum!" then another, and still another. Every man sprung to his feet as if struck by an electric shock, and we
looked inquiringly into one another's faces. "What is that?" asked every one but no one answered. Those heavy booms then came
thicker and faster, and just a few seconds after we heard that first dull, ominous growl off to the southwest, came a low,
sullen, continuous roar. There was no mistaking that sound. That was not a squad of pickets emptying their guns on being relieved
from duty; it was the continuous roll of thousands of muskets, and told us that a battle was on.
What I have been describing just now occurred during a few seconds only, and
with the roar of musketry the long roll began to beat in our camp. Then ensued a scene of desperate haste, the like of which
I certainly had never seen before, nor ever saw again. I remember that in the midst of this terrible uproar and confusion,
while the boys were buckling on their cartridge boxes, and before even the companies had been formed, a mounted staff officer
came galloping wildly down the line from the right. He checked and whirled his horse sharply around right in our company street,
the iron-bound hoofs of his steed crashing among the tin plates lying in a little pile where my mess had eaten its breakfast
that morning. The horse was flecked with foam and its eyes and nostrils were red as blood. The officer cast one hurried glance
around him, and exclaimed: "My God! this regiment not in line yet! They have been fighting on the right over an hour!" And
wheeling his horse, he disappeared in the direction of the colonel's tent...
Well, the companies were formed, we marched out on the regimental parade ground,
and the regiment was formed in line. The command was given: "Load at will; load!" We had anticipated this, however, as the
most of us had instinctively loaded our guns before we had formed company. All this time the roar on the right was getting
nearer and louder. Our old colonel rode up close to us, opposite the center of the regimental line, and called out, "Attention,
battalion! " We fixed our eyes on him to hear what was coming. It turned out to be the old man's battle harangue.
"Gentlemen," said he, in a voice that every man in the regiment heard, "remember
your State, and do your duty today like brave men."
That was all... Immediately after the colonel had given us his brief exhortation,
the regiment was marched across the little field I have before mentioned, and we took our place in line of battle, the woods
in front of us, and the open field in our rear. We "dressed on" the colors, ordered arms, and stood awaiting the attack. By
this time the roar on the right had become terrific. The Rebel army was unfolding its front, and the battle was steadily advancing
in our direction. We could begin to see the blue rings of smoke curling upward among the trees off to the right, and the pungent
smell of burning gun-powder filled the air. As the roar came travelling down the line from the right it reminded me (only
it was a million times louder) of the sweep of a thunder-shower in summer-time over the hard ground of a stubble-field.
And there we stood, in the edge of the woods, so still, waiting for the storm
to break on us...
The time we thus stood, waiting the attack, could not have exceeded five minutes.
Suddenly, obliquely to our right, there was a long, wavy flash of bright light, then another, and another! It was the sunlight
shining on gun barrels and bayonets--and--there they were at last! A long brown line, with muskets at a right shoulder shift,
in excellent order, right through the woods they came.
We began firing at once. From one end of the regiment to the other leaped
a sheet of red flame, and the roar that went up from the edge of that old field doubtless advised General Prentiss of the
fact that the Rebels had at last struck the extreme left of his line. We had fired but two or three rounds when, for some
reason,--I never knew what,--we were ordered to fall back across the field, and did so. The whole line, so far as I could
see to the right, went back. We halted on the other side of the field, in the edge of the woods, in front of our tents, and
again began firing. The Rebels, of course, had moved up and occupied the line we had just abandoned. And here we did our first
hard fighting during the day. Our officers said, after the battle was over, that we held this line an hour and ten minutes.
How long it was I do not know. I "took no note of time."
We retreated from this position as our officers afterward said, because the
troops on our right had given way, and we were flanked. Possibly those boys on our right would give the same excuse for their
leaving, and probably truly, too. Still, I think we did not fall back a minute too soon. As I rose from the comfortable log
from behind which a bunch of us had been firing, I saw men in gray and brown clothes, with trailed muskets, running through
the camp on our right, and I saw something else, too, that sent a chill all through me. It was a kind of flag I had never
seen before. It was a gaudy sort of thing, with red bars. It flashed over me in a second that that thing was a Rebel flag.
It was not more than sixty yards to the right. The smoke around it was low and dense and kept me from seeing the man who was
carrying it, but I plainly saw the banner. It was going fast, with a jerky motion, which told me that the bearer was on a
double-quick. About that time we left. We observed no kind of order in leaving; the main thing was to get out of there as
quick as we could. I ran down our company street, and in passing the big Sibley tent of our mess I thought of my knapsack
with all my traps and belongings, including that precious little packet of letters from home. I said to myself, "I will save
my knapsack, anyhow;" but one quick backward glance over my left shoulder made me change my mind, and I went on. I never saw
my knapsack or any of its contents afterwards.
Our broken forces halted and re-formed about half a mile to the rear of our
camp on the summit of a gentle ridge, covered with thick brush. I recognized our regiment by the little gray pony the old
colonel rode, and hurried to my place in the ranks. Standing there with our faces once more to the front, I saw a seemingly
endless column of men in blue, marching by the flank, who were filing off to the right through the woods, and I heard our
old German adjutant, Cramer, say to the colonel, "Dose are de troops of Sheneral Hurlbut. He is forming a new line dere in
de bush." I exclaimed to myself from the bottom of my heart, "Bully for General Hurlbut and the new line in the bush! Maybe
we'll whip 'em yet." I shall never forget my feelings about this time. I was astonished at our first retreat in the morning
across the field back to our camp, but it occurred to me that maybe that was only "strategy" and all done on purpose; but
when we had to give up our camp, and actually turn our backs and run half a mile, it seemed to me that we were forever disgraced,
and I kept thinking to myself: "What will they say about this at home?"
I was very dry for a drink, and as we were doing nothing, just then, I slipped
out of ranks and ran down to the little hollow in our rear, in search of water. Finding a little pool, I threw myself on the
ground and took a copious draught. As I rose to my feet, I observed an officer about a rod above me, also quenching his thirst,
holding his horse meanwhile by the bridle. As he rose I saw it was our old adjutant. At no other time would I have dared accost
him unless in the line of duty, but the situation made me bold.
"Adjutant," I said, "What does this mean--our having to run this way? Ain't
we whipped?"
He blew the water from his mustache, and quickly answered in a careless way:
"Oh, no; dat is all ride. We yoost fall back to form on the reserve. Sheneral Buell vas now crossing der river mit 50,000
men, and vill be here pooty quick; and Sheneral Lew Vallace is coming up from Crump's Landing mit 15,000 more. Ve vips 'em;
ve vips 'em. Go to your gompany." ... But as the long hours wore on that day, and still Buell and Wallace did not come, my
faith in the adjutant's veracity became considerably shaken.
It was at this point that my regiment was detached from Prentiss' division
and served with it no more that day. We were sent some distance to the right to support a battery, the name of which I never
learned. It was occupying the summit of a slope, and was actively engaged when we reached it. We were put in position of about
twenty rods in the rear of the battery, and ordered to lie flat on the ground. The ground sloped gently down in our direction,
so that by hugging it close, the rebel shot and shell went over us.
It was here, at about ten o'clock in the morning, that I first saw Grant that
day. He was on horseback, of course, accompanied by his staff, and was evidently making a personal examination of his lines.
He went by us in a gallop, riding between us and the battery, at the head of his staff. The battery was then hotly engaged;
shot and shell were whizzing overhead, and cutting off the limbs of trees, but Grant rode through the storm with perfect indifference,
seemingly paying no more attention to the missiles than if they had been paper wads.
We remained in support of this battery until about 2 o'clock in the afternoon.
We were then put in motion by the right flank, filed to the left, crossed the left-hand Corinth road; then we were thrown
into the line by the command: "By the left flank, march." We crossed a little ravine and up a slope, and relieved a regiment
on the left of Hurlbut's line. This line was desperately engaged, and had been at this point, as we afterwards learned, for
fully four hours. I remember as we went up the slope and began firing, about the first thing that met my gaze was what out
West we would call a "windrow" of dead men in blue; some doubled up face downward, others with their white faces upturned
to the sky, brave boys who had been shot to death in "holding the line." Here we stayed until our last cartridge was shot
away. We were then relieved by another regiment. We filled our cartridge boxes again and went back to the support of our battery.
The boys laid down and talked in low tones. Many of our comrades alive and well an hour ago, we had left dead on that bloody
ridge. And still the battle raged. From right to left, everywhere, it was one never-ending, terrible roar, with no prospect
of stopping.
Somewhere between 4 and 5 o'clock, as near as I can tell, everything became
ominously quiet. Our battery ceased firing; the gunners leaned against the pieces and talked and laughed. Suddenly a staff
officer rode up and said something in a low tone to the commander of the battery, then rode to our colonel and said something
to him. The battery horses were at once brought up from a ravine in the rear, and the battery limbered up and moved off through
the woods diagonally to the left and rear. We were put in motion by the flank and followed it. Everything kept so still, the
loudest noise I heard was the clucking of the wheels of the gun-carriages and caissons as they wound through the woods. We
emerged from the woods and entered a little old field. I then saw at our right and front lines of men in blue moving in the
same direction we were, and it was evident that we were falling back.
All at once, on the right, the left, and from our recent front, came one tremendous
roar, and the bullets fell like hail. The lines took the double-quick towards the rear. For awhile the attempt was made to
fall back in order, and then everything went to pieces. My heart failed me utterly. I thought the day was lost. A confused
mass of men and guns, caissons, army wagons, ambulances, and all the debris of a beaten army surged and crowded along the
narrow dirt road to the landing, while that pitiless storm of leaden hail came crashing on us from the rear. It was undoubtedly
at this crisis in our affairs that the division of General Prentiss was captured...
It must have been when we were less than half a mile from the landing on our
disorderly retreat before mentioned, that we saw standing in line of battle, at ordered arms, extending from both sides of
the road until lost to sight in the woods, a long well-ordered line of men in blue. What did that mean? and where had they
come from? I was walking by the side of Enoch Wallace, the orderly sergeant of my company. . . . Even he, in the face of this
seemingly appalling state of things, had evidently lost heart.
I said to him: "Enoch, what are those men there for?"
He answered in a low tone: "I guess they are put there to hold the Rebels
in check till the army can get across the river."
And doubtless that was the thought of every intelligent soldier in our beaten
column. And yet it goes to show how little the common soldier knew of the actual situation. We did not know then that this
line was the last line of battle of the "Fighting Fourth Division" under General Hurlbut; that on its right was the division
of McClernand, the Fort Donelson boys; that on its right, at right angles to it, and, as it were, the refused wing of the
army, was glorious old Sherman, hanging on with a bulldog grip to the road across Snake Creek from Crump's Landing by which
Lew Wallace was coming with 5,000 men. In other words, we still had an unbroken line confronting the enemy, made up of men
who were not yet ready, by any manner of means, to give up that they were whipped...
Well, we filed through Hurlbut's line, halted, re-formed, and faced to the
front once more. We were put in place a short distance in the rear of Hurlbut, as a support to some heavy guns. It must have
been about five o'clock now. Suddenly, on the extreme left, and just a little above the Ianding, came a deafening explosion
that fairly shook the ground beneath our feet, followed by others in quick and regular succession. The look of wonder and
inquiry that the soldiers' faces wore for a moment disappeared for one of joy and exultation as it flashed across our minds
that the gunboats had at last joined hands in the dance, and were pitching big twenty-pound Parrott shells up the ravine in
front of Hurlbut, to the terror and discomfiture of our adversaries.
The last place my regiment assumed was close to the road coming up from the
landing. As we were lying there I heard the strains of martial music and saw a body of men marching by the flank up the road.
I slipped out of ranks and walked out to the side of the road to see what troops they were. Their band was playing "Dixie's
Land," and playing it well. The men were marching at a quick step, carrying their guns, cartridge-boxes, haversacks, canteens,
and blanket-rolls. I saw that they had not been in the fight, for there was no powder-smoke on their faces. "What regiment
is this?" I asked of a young sergeant marching on the flank. Back came the answer in a quick, cheery tone. "The 36th Indiana,
the advance guard of Buell's army."
I did not, on hearing this, throw my cap into the air and yell. That would
have given those Indiana fellows a chance to chaff and guy me, and possibly make sarcastic remarks, which I did not care to
provoke. I gave one big, gasping swallow and stood still, but the blood thumped in the veins of my throat and my heart fairly
pounded against my little infantry jacket in the joyous rapture of this glorious intelligence. Soldiers need not be told of
the thrill of unspeakable exultation they have all felt at the sight of armed friends in danger's darkest hour. Speaking for
myself alone, I can only say, in the most heart-felt sincerity, that in all my obscure military career, never to me was the
sight of reinforcing legions so precious and so welcome as on that Sunday evening when the rays of the descending sun were
flashed back from the bayonets of Buell's advance column as it deployed on the bluffs of Pittsburg Landing.
Recommended
Reading: Shiloh and the Western Campaign
of 1862. Review: The bloody and decisive two-day
battle of Shiloh (April 6-7, 1862) changed the entire course of the American Civil War. The
stunning Northern victory thrust Union commander Ulysses S. Grant into the national spotlight, claimed the life of Confederate
commander Albert S. Johnston, and forever buried the notion that the Civil War would be a short conflict. The conflagration
at Shiloh had its roots in the strong Union advance during the winter of 1861-1862 that resulted in the capture of Forts Henry
and Donelson in Tennessee. Continued below…
The offensive collapsed General Albert S. Johnston advanced line in Kentucky and forced him to withdraw all
the way to northern Mississippi. Anxious to attack the enemy,
Johnston began concentrating Southern forces at Corinth, a major
railroad center just below the Tennessee border. His bold
plan called for his Army of the Mississippi to march north and destroy General Grant's Army
of the Tennessee before it could link up with another Union
army on the way to join him. On the morning of April 6, Johnston boasted to his subordinates,
"Tonight we will water our horses in the Tennessee!" They
nearly did so. Johnston's sweeping attack hit the unsuspecting Federal camps at Pittsburg Landing
and routed the enemy from position after position as they fell back toward the Tennessee River.
Johnston's sudden death in the Peach Orchard, however, coupled
with stubborn Federal resistance, widespread confusion, and Grant's dogged determination to hold the field, saved the Union
army from destruction. The arrival of General Don C. Buell's reinforcements that night turned the tide of battle. The next
day, Grant seized the initiative and attacked the Confederates, driving them from the field. Shiloh
was one of the bloodiest battles of the entire war, with nearly 24,000 men killed, wounded, and missing. Edward Cunningham,
a young Ph.D. candidate studying under the legendary T. Harry Williams at Louisiana
State University, researched and wrote Shiloh and the Western Campaign of 1862 in 1966. Although it remained unpublished, many Shiloh
experts and park rangers consider it to be the best overall examination of the battle ever written. Indeed, Shiloh
historiography is just now catching up with Cunningham, who was decades ahead of modern scholarship. Western Civil War historians
Gary D. Joiner and Timothy B. Smith have resurrected Cunningham's beautifully written and deeply researched manuscript from
its undeserved obscurity. Fully edited and richly annotated with updated citations and observations, original maps, and a
complete order of battle and table of losses, Shiloh and the Western Campaign of 1862 will
be welcomed by everyone who enjoys battle history at its finest. Edward Cunningham, Ph.D., studied under T. Harry Williams
at Louisiana State
University. He was the author of The Port Hudson Campaign: 1862-1863
(LSU, 1963). Dr. Cunningham died in 1997. Gary D. Joiner, Ph.D. is the author of One Damn Blunder from Beginning to End: The
Red River Campaign of 1864, winner of the 2004 Albert Castel Award and the 2005 A. M. Pate, Jr., Award, and Through the Howling
Wilderness: The 1864 Red River Campaign and Union Failure in the West. He lives in Shreveport,
Louisiana. About the Author: Timothy B. Smith, Ph.D., is author of Champion Hill:
Decisive Battle for Vicksburg (winner of the 2004 Mississippi
Institute of Arts and Letters Non-fiction Award), The Untold Story of Shiloh: The Battle and the Battlefield, and This Great
Battlefield of Shiloh: History, Memory, and the Establishment of a Civil War National Military Park. A former ranger at Shiloh,
Tim teaches history at the University of Tennessee.
Recommended Reading: Shiloh: The Battle That Changed the Civil
War (Simon & Schuster). From Publishers Weekly: The bloodbath at Shiloh, Tenn. (April 6-7, 1862), brought
an end to any remaining innocence in the Civil War. The combined 23,000 casualties that the two armies inflicted on each other
in two days shocked North and South alike. Ulysses S. Grant kept his head and managed, with reinforcements, to win a hard-fought
victory. Continued below…
Confederate
general Albert Sidney Johnston was wounded and bled to death, leaving P.G.T. Beauregard to disengage and retreat with a dispirited
gray-clad army. Daniel (Soldiering in the Army of Tennessee) has crafted a superbly researched volume that will appeal to
both the beginning Civil War reader as well as those already familiar with the course of fighting in the wooded terrain bordering
the Tennessee River.
His impressive research includes the judicious use of contemporary newspapers and extensive collections of unpublished letters
and diaries. He offers a lengthy discussion of the overall strategic situation that preceded the battle, a survey of the generals
and their armies and, within the notes, sharp analyses of the many controversies that Shiloh
has spawned, including assessments of previous scholarship on the battle. This first new book on Shiloh
in a generation concludes with a cogent chapter on the consequences of those two fatal days of conflict.
Recommended Reading: Shiloh--In Hell before Night. Description: James McDonough has written a good, readable and concise history of a battle that the author
characterizes as one of the most important of the Civil War, and writes an interesting history of this decisive 1862 confrontation
in the West. He blends first person and newspaper accounts to give the book a good balance between the general's view and
the soldier's view of the battle. Continued below…
Particularly
enlightening is his description of Confederate General Albert Sidney Johnston, the commander who was killed on the first day
of the battle. McDonough makes a pretty convincing argument that Johnston
fell far short of the image that many give him in contemporary and historical writings. He is usually portrayed as an experienced
and decisive commander of men. This book shows that Johnston was a man of modest war and command experience, and that he rose to prominence shortly before
the Civil War. His actions (or inaction) prior to the meeting at Shiloh -- offering to let his subordinate Beauregard take
command for example -- reveal a man who had difficulty managing the responsibility fostered on him by his command. The author
does a good job of presenting several other historical questions and problems like Johnston's reputation vs. reality that really add a lot of interest to the pages.
Recommended Reading: Seeing
the Elephant: RAW RECRUITS AT THE BATTLE OF SHILOH. Description: One of the bloodiest battles in the Civil War, the
two-day engagement near Shiloh, Tennessee,
in April 1862 left more than 23,000 casualties. Fighting alongside seasoned veterans were more than 160 newly recruited regiments
and other soldiers who had yet to encounter serious action. In the phrase of the time, these men came to Shiloh
to "see the elephant". Continued below…
Drawing on
the letters, diaries, and other reminiscences of these raw recruits on both sides of the conflict, "Seeing the Elephant" gives
a vivid and valuable primary account of the terrible struggle. From the wide range of voices included in this volume emerges
a nuanced picture of the psychology and motivations of the novice soldiers and the ways in which their attitudes toward the
war were affected by their experiences at Shiloh.
Recommended Reading: The Battle
of Shiloh and the Organizations Engaged (Hardcover). Description: How can an essential "cornerstone of Shiloh
historiography" remain unavailable to the general public for so long? That's what I kept thinking as I was reading this reprint
of the 1913 edition of David W. Reed's “The Battle of Shiloh and the Organizations Engaged.” Reed, a veteran of
the Battle of Shiloh and the first historian of the Shiloh National Military Park,
was tabbed to write the official history of the battle, and this book was the result. Reed wrote a short, concise history
of the fighting and included quite a bit of other valuable information in the pages that followed. The large and impressive
maps that accompanied the original text are here converted into digital format and included in a CD located within a flap
at the back of the book. Author and former Shiloh Park Ranger Timothy Smith is responsible for bringing this important reference
work back from obscurity. His introduction to the book also places it in the proper historical framework. Continued below…
Reed's history of the campaign and battle covers only seventeen pages and is meant to
be a brief history of the subject. The detail is revealed in the rest of the book. And what detail there is! Reed's order
of battle for Shiloh
goes down to the regimental and battery level. He includes the names of the leaders of each organization where known, including
whether or not these men were killed, wounded, captured, or suffered some other fate. In a touch not often seen in modern
studies, the author also states the original regiment of brigade commanders. In another nice piece of detail following the
order of battle, staff officers for each brigade and higher organization are listed. The book's main point and where it truly
shines is in the section entitled "Detailed Movements of Organizations". Reed follows each unit in their movements during
the battle. Reading this section along with referring to the computerized maps gives one a solid foundation for future study
of Shiloh. Forty-five pages cover the brigades of all three armies present at Shiloh.
Wargamers and buffs will love the "Abstract of Field Returns". This section lists Present
for Duty, engaged, and casualties for each regiment and battery in an easy to read table format. Grant's entire Army of the
Tennessee has Present for Duty strengths. Buell's Army of
the Ohio is also counted well. The Confederate Army of the
Mississippi is counted less accurately, usually only going
down to brigade level and many times relying only on engaged strengths. That said, buy this book if you are looking for a
good reference work for help with your order of battle.
In what I believe is an unprecedented move in Civil War literature, the University of Tennessee Press made the somewhat
unusual decision to include Reed's detailed maps of the campaign and battle in a CD which is included in a plastic sleeve
inside the back cover of the book. The cost of reproducing the large maps and including them as foldouts or in a pocket in
the book must have been prohibitive, necessitating this interesting use of a CD. The maps were simple to view and came in
a PDF format. All you'll need is Adobe Acrobat Reader, a free program, to view these. It will be interesting to see if other
publishers follow suit. Maps are an integral part of military history, and this solution is far better than deciding to include
poor maps or no maps at all. The Read Me file that came with the CD relays the following information:
-----
The maps contained on this CD are scans of the original oversized maps printed in the
1913 edition of D. W. Reed's The Battle of Shiloh and the Organizations Engaged. The original maps, which were in a very large
format and folded out of the pages of this edition, are of varying sizes, up to 23 inches by 25 inches. They were originally
created in 1901 by the Shiloh National
Military Park under the direction
of its historian, David W. Reed. They are the most accurate Shiloh battle maps in existence.
The maps on the CD are saved as PDF (Portable Document Format) files and can be read
on any operating system (Windows, Macintosh, Linux) by utilizing Adobe Acrobat Reader. Visit http://www.adobe.com to download
Acrobat Reader if you do not have it installed on your system.
Map 1. The Field of Operations from Which the Armies Were Concentrated at Shiloh, March and April 1862
Map 2. The Territory between Corinth, Miss.,
and Pittsburgh Landing, Tenn., Showing Positions and Route
of the Confederate Army in Its Advance to Shiloh, April 3, 4, 5, & 6, 1862
Map 3. Positions on the First Day, April 6, 1862
Map 4. Positions on the Second Day, April 7, 1862
Complete captions appear on the maps.
-----
Timothy Smith has done students of the Civil War an enormous favor by republishing
this important early work on Shiloh. Relied on for generations by Park Rangers and other
serious students of the battle, The Battle of Shiloh and the Organizations Engaged has been resurrected for a new generation
of Civil War readers. This classic reference work is an essential book for those interested in the Battle of Shiloh. Civil
War buffs, wargamers, and those interested in tactical minutiae will also find Reed's work to be a very good buy. Highly recommended.
|

